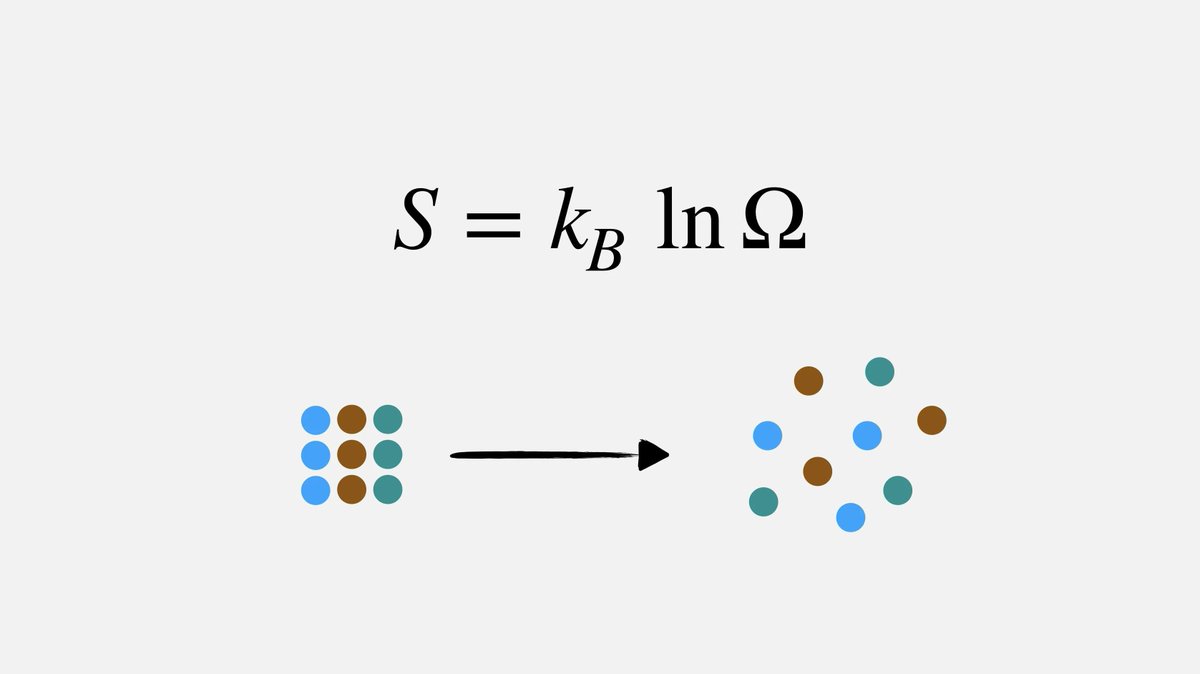Termodinámica
En 2022 con LOMLOE se trata en 1º Bachillerato, ver apuntes elaboración propia 1º Bachillerato, en concreto
Pizarras termodinámica, aparte de lo asociado a termoquímica.
twitter _luigiruffolo/status/1227485996465491968
One of the best book openings ever (via Johnson Shrestha)
Goodstein’s ‘States of Matter’ Opening Quote - truthorfiction.com
The four laws of thermodynamics The Royal Institution - youtube
Al hablar de termodinámica normalmente se asocia a física; se suele introducir en primeros cursos universitarios y en bachillerato se trata en Tecnología Industrial.
Existen conceptos relacionados con química como la entropía y la termoquímica.
Asociable a bloque de Química de 2º de Bachillerato, pendiente añadir y separar información (entropía, leyes de la termodinámica …); se trata en los apuntes de elaboración propia de Química de 2º de Bachillerato
Se pueden asociar conceptos generales y puede haber información dentro de recursos sobre energía , trabajo y calor.
En la serie de vídeos “universo mecánico” el capítulo 47 trata la entropía, y tiene estas frases iniciales de resumen geniales
La ciencia de la termodinámica se basa en cuatro postulados fundamentales o axiomas, llamados los cuatro primeros principios de la termodinámica.
De esos 4 principios, el 2º fue el 1º que se descubrió, el 1º fue el 2º en descubrirse, el 3er principio que se descubrió se llama principio 0, y el 4º se llama 3er principio.
Pero todo eso tiene perfecto sentido, porque la termodinámica es la más implacablemente lógica de todas las ciencias.
Les diré brevemente lo que son esos cuatro principios:
El principio cero dice precisamente que la temperatura tiene sentido
El primero es la conservación de la energía
El segundo principio es el principio de la entropía
El tercer principio dice que hay una temperatura tan baja que nunca se puede alcanzar
“Dr. David L. Goodstein, California Institute of Tecnology.
Apuntes
Termoquímica - selectividadonline (archive.org) Eduardo Montoya Marín, cc-by-nc-sa
Termodinámica, primer principio
Termodinámica, segundo principio
Teresa Martín Blas y Ana Serrano Fernández - Universidad Politécnica de Madrid (UPM).
Apuntes de termodinámica elemental E. Barrull, 1994
©* Biopsychology.org, 1998 - 2006. Consultado en enero 2021 su última actualización de 2006
Silvia Pérez Casas, Cálculo propiedades termodinámicas para substancias puras. Tiene “Interludio Matemático” inicial interesante
Thermodynamics, Professor Z. S. Spakovszky, Fall 2008, MIT
Libros sobre Ingeniería Energética, CopyrightPedro Fernández Díez
Termodinámica técnica
Tecnologia industrial (autoformació IOC) > Màquines > Termodinàmica - educaciodigital.cat
Ejercicios
Problemas resueltos de termodinámica, Física con ordenador
Ángel Franco García
Problemas y ejercicios resueltos de Termodinámica I (waybakmachine, no operativo en 2021)
http://juliweb.es/ (waybackmachine, no operativo en 2021)
Julián Moreno Mestre
Examen de Termodinámica I Junio 2004, Industriales ETSII, UPM
Collection of Solved Problems in Physics - thermodynamics - physicstasks.eu
This collection of Solved Problems in Physics is developed by Department of Physics Education, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague since 2006.
The Collection contains tasks at various level in mechanics, electromagnetism, thermodynamics and optics. The tasks mostly do not contain the calculus (derivations and integrals), on the other hand they are not simple such as the use just one formula. Tasks have very detailed solution descriptions. Try to solve the task or at least some of its parts independently. You can use hints and task analysis (solution strategy).
Difficulty level
Level 1 – Lower secondary level
Level 2 – Upper secondary level
Level 3 – Advanced upper secondary level
Level 4 – Undergraduate level
Cuestiones y problemas resueltos de Termodinámica técnica - upv.es
Convenio de signos Q y W
Convenio IUPAC
First law of thermodynamics, description - Wikipedia
Se cita Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry (IUPAC Green Book) See Sec. 2.11 Chemical Thermodynamics
Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry (IUPAC Green Book) 3rd Edition 2ndPrinting 22apr2011 PDF
IUPAC Green Book, Quantities, Units, and Symbols in Physical Chemistry
Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry (IUPAC Green Book), 3rd Edition 2012 2ndPrinting PDF
Se indica
(1)… The given equation in integrated form is ΔU=Q+W. Q>0 and W>0 indicate an increase in the energy of the system
laplace.us.es, Trabajo en termodinámica (GIE), Convenio de signos
El convenio en el que ΔU=Q-W es más antiguo y se suele llamar el convenio de Clausius. Lo cito en resolución de problemas de oposiciones de termodinámica
laplace.us.es, Primer principio de la termodinámica (GIE)
oscardeabril.aq.upm.es Tema 9 Primer principio de la termodinamica.pdf
Página 3
Convenio termodinámico o de Clausius*
del sistema en el entorno:
W > 0 → lo realiza el sist.
W < 0 → se realiza sobre el sist.
Convenio mecánico o de la IUPAC**
del entorno en el sistema:
W > 0 → se realiza sobre el sist.
W < 0 → lo realiza el sist.
*El convenio de Clausius es más adecuado para el estudio de máquinas térmicas, ya que el trabajo útil se trata como positivo. **El convenio de la IUPAC (o tradicional) es el utilizado en mecánica
twitter memecrashes/status/1670563581757214724
Unidades de temperatura
Resolution 3 of the 13th CGPM (1967). SI unit of thermodynamic temperature (kelvin)
COMPTES RENDUS DES SÉANCES TREIZIÈME CONFÉRENCE GÉNÉRALE DES POIDS ET MESURES
1º l’unité de température thermodynamique est désignée sous le nom “kelvin” et son symbole est K;
2º ce même nom et ce même symbole sont utilisés pour exprimer un intervalle de température;
3º l’unité de température thermodynamique ne sera plus désignée sous le nom “degré Kelvin”, symbole ºK;
Real Decreto 2032/2009, de 30 de diciembre, por el que se establecen las unidades legales de medida.
Tabla 1 Unidades SI básicas
Magnitud, Nombre de la unidad, Símbolo de la unidad
temperatura termodinámica, kelvin, K
Green Book. Quantities, Units, and Symbols in Physical Chemistry
The SI unit of Celsius temperature is the degree Celsius, ◦C, which is equal to the kelvin, K. ◦C shall be treated as a single symbol, with no space between the ◦ sign and the C. The symbol ◦K, and the symbol ◦, shall no longer be used for the unit of thermodynamic temperature.
ISO 80000-5. Quantities and units — Part 5: Thermodynamics
The units of thermodynamic and Celsius temperature difference or change are identical. Such differences or changes may be expressed either in kelvins, symbol K, or in degrees Celsius, symbol, ºC.
It should be noted that the symbol for the degree Celsius shall be preceded by a space (see ISO 31-0, 3.4).
Definición de temperatura. Temperaturas negativas
A nivel de secundaria y bachillerato se asume el 0 K como un valor límite, pero se puede abrir la mente, la temperatura es una definición estadística y asociada a ciertas situaciones …
Qué significa que un gas cuántico tiene una temperatura negativa
Francis en Naukas (con adenda): Qué significa que un gas cuántico tiene una temperatura negativa
Cito:
En un sistema fuera del equilibrio el concepto de temperatura no está bien definido, luego puede ser positiva, nula e incluso negativa. ¿Puede tener un sistema en equilibrio termodinámico una “temperatura negativa,” por ejemplo, un gas cuántico ultrafrío? Por supuesto, todo depende, de qué depende, depende de la definición de temperatura que se utilice
twitter gregeganSF/status/1540950512186429442
[1/16] You might have heard it claimed that the temperature of a system is an “emergent” property that only makes sense if the system has a large number of degrees of freedom. This isn’t true!
There are certainly things that can be said about the temperature of a system that are
[2/16] only approximately true, in general, but become vastly better approximations for systems with many degrees of freedom. But temperature itself is perfectly well defined, regardless.
In classical mechanics, suppose we have a system with f degrees of freedom whose total
[3/16] energy is known to lie between E and E+δE. Maybe we know some other things about it. But when we describe the system in phase space — the abstract space that has one dimension for the coordinate and one for the momentum associated with each of the f degrees of freedom —
[4/16] suppose we can only say that the system lies in some subset of this 2f-dimensional space that’s also a 2f-dimensional set.
For example, for a single particle in 3 dimensions, we haven’t pinned the system down to a point, or a line, etc., in its 6-dimensional phase space.
…
It’s worth adding that our definition of temperature allows for negative temperatures.
For example, suppose we have a set of particles fixed in place but free to switch their spins from parallel to antiparallel to a magnetic field. Their total energy will depend on the direction
of their spins, but it can’t increase without bound, and near the maximum energy, adding more energy shrinks the possible states the system can be in. So dΩ/dE will be negative.
But when one temperature is -ve and another +ve:
T1 T2 < 0
and energy will flow from the system
with negative temperature to the one with positive temperature, because it’s
[T1-T2]/ (T1 T2)
that must be positive, for energy to flow from system 1 to system 2.
This makes systems with negative temperature act as if they’re “hotter” than any system with positive temperature.
Vídeos
The four laws of thermodynamics, The Royal Institution, playlist
Referencias
http://kinetics.nist.gov/janaf/
Primer principio
Termodinámica, primer principio
laplace.us.es, Primer principio de la termodinámica (GIE)
laplace.us.es Problemas del primer principio de la termodinámica (GIE)
chemwiki.ucdavis.edu The First Law of Thermodynamics
Segundo principio
montes.upm.es, Termodinámica, primer principio
laplace.us.es, Segundo Principio de la Termodinámica
twitter fermatslibrary/status/1532718253365202945
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
The entropy, also known disorder, of a system will increase over time.
The Universe is full of irreversible processes that continuously increase its total entropy thus tending to disorder rather than order.
Procesos termodinámicos
¿Qué es el proceso termodinámico? Definición - thermal-engineering.org
Isocórico (V=cte)
Isobárico (P=cte)
Adiabático (Q=0)
Isotérmico (T=cte)
[Entropía]((/home/recursos/entropia)
Ciclo de Carnot
laplace.us.es, Ciclo de Carnot
Máquinas térmicas
El ciclo de Carnot es una máquina térmica ideal
Máquinas térmicas - montes.upm.es
Ciclo Otto: motores de combustión interna de gasolina encendido provocado
En aproximación teórica todo el calor se aporta a volumen constante.
Ciclo de Otto - edithyurani12
EL CICLO OTTO - navarraof.orgfree.com
Motor de cuatro tiempos encendido por chispa – Ciclo Otto - stefanelli.eng.br Incluye animación
Ciclo Otto y ciclo diesel slideshare
Ciclo diesel: motores de combustión interna gasoil encendido por compresión
Qué es el ciclo diesel – Motor diesel – Definición - thermal-engineering.org
U2 análisis termodinámico del motor diesel - tecsup, slideshare
Motor de cuatro tiempos de inyección de combustible – Ciclo Diesel - stefanelli.eng.br Incluye animación
Ciclo Brayton: turbinas de gas
Brayton cycle - wikipedia.org
Memes
twitter FIKASI1/status/1486453449919184896
Mañana trabajaremos en tecnología industrial este meme para introducir algunos principios termodinámicos. Interesante para la época COVID con tanta ventana abierta en clase…
Simulaciones
Simulador termodinámico
Termograf.unizar.es
Ejecutable windows y mutiplataforma